

Umaima Shah
Sat Feb 07 2026
10 mins Read
Kling AI officially launched its Kling 3.0 model series on February 5, 2026, and it quickly dominated creator conversations. This comparison puts Kling 3.0 head-to-head with Kling 2.6 to examine how the upgrade changes real production workflows, especially multi-shot video and in-model editing.
You want to recreate a character, preserve the mood, and control camera behavior without fighting the model. That’s exactly what we did before writing this: test, evaluate, and repeat.
This blog focuses on performance to evaluate the features and the hype. We break down
- What changed in Kling 3.0
- How it compares to Kling 2.6
- Where each model performs better in practical creator workflows.
Kling 3.0 vs Kling 2.6: Quick Verdict
If you want a fast answer before diving into the deep comparison, here’s the practical breakdown.
- Kling 2.6: cinematic quality with native audio, but affordable
- Kling 3.0: longer duration multishot videos with video-editing capabilities within the model, but expensive
- Both models: can be tested side by side for workflow optimization inside ImagineArt AI Video Generator
This blog explains why these differences matter and how you can test them yourself.
1) Kling 3.0 Highlights
Kling 3.0 landed as a make-or-break upgrade because it targets the exact friction points creators kept hitting in AI video generation. The conversation isn’t abstract. It’s about visible fixes in clips that used to fall apart under scrutiny.
Kling 3.0 shows up strongest in areas that used to break immersion:
- Multi-shot prompting: connects up to six structured shots into a single sequence, allowing creators to build coherent mini-stories instead of isolated clips
- AI director: adds guided camera and scene control that keeps shot progression intentional rather than random
- Multi-image references for image to video: anchors scenes to multiple visual references, improving consistency across characters and environments
- Character consistency: fewer face morphs and identity shifts between frames
- Wardrobe and prop stability: clothing and objects stay locked instead of drifting mid-scene
- Scene continuity: smoother transitions in camera motion and pacing
- Refinement control: edits feel more surgical, with fewer full regenerations
Kling 2.6 already ran a stable workflow and proved that creators could build repeatable pipelines. Kling 3.0 steps onto that stage and stretches the margins. It focuses less on flashy upgrades and more on tightening the details that decide whether a clip survives real production.
 Kling 2.6 vs 3.0, Which version is better!
Kling 2.6 vs 3.0, Which version is better!
2) Kling 3.0 Features
This is where Kling 3.0 stops sounding like a spec sheet and starts feeling like a real upgrade. After testing it side by side, the changes show up in how the clips behave when you push them, not just in feature labels.
Here’s what stands out.
Multi-Shot Scenes
Kling 3.0 advances clip structure with multi-shot generation and extends video duration to 15 seconds.
- In Kling 2.6, stitching scenes always carried a small reset feeling. With 3.0, sequences connect in a way that feels intentional.
- The jump to 15-second clips gives scenes breathing room instead of rushing transitions.
- Continuity holds across shots, so sequences feel planned rather than assembled.
👑 Kling 3.0 - The Real KING
— ImagineArt (@ImagineArt_X) February 4, 2026
🎠 Multi-prompt video (up to 15s)
🎧 Audio reference
🔍 Macro close-ups + video editing
🔥 86% OFF and Kling 3.0 Unlimited (limited time)
RT + reply “Kling30” to win 300 credits pic.twitter.com/zWe8AnmatC
Perfect Audio Sync
The dialogue sync in Kling 3.0 is a chef’s kiss.
- The audio sync locks in tighter, and multilingual output doesn’t feel like a side feature.
- Dialogue sits inside the motion instead of floating over it.
- You can specify in a group of four who speaks what, when, how,, and in which language
- For creators working in ads or storytelling, this reduces post-editing overhead.
Character Consistency
Character stability is where Kling 3.0 pushes hardest. Strong competitors already compete in this space, but Kling 3.0 tightens identity persistence to the point where it carries across shots with fewer visible breaks.
- Faces stay stable between frames
- Expressions evolve without morphing
- Kling 3.0 edges ahead of strong competitors by tightening identity control.
This is the layer that decides if a model works in production.
Native 4K Output
Kling 3.0 delivers native 4K output without relying on external upscalers.
- Textures render sharper at the source
- Fine details survive compression
- Motion sequences stay stable at high resolution
High fidelity now sits inside the generation step, not as an afterthought.
Directed Camera Control
Camera behavior feels more intentional. Kling 3.0 responds to prompts like a directed system rather than a random-motion engine.
- Pans and tilts follow prompt instructions
- Zooms feel deliberate, not accidental
- Motion reads like planned cinematography
This gives creators more authorship over scene language.
Improved Presets
Presets in Kling 3.0 arrive more refined and predictable.
- Styles lock in faster
- Rendering artifacts drop in complex motion
- Visual tone holds across frames
If you want to test these Kling 3.0 features yourself without switching platforms, you can run both models inside the ImagineArt AI Video Generator.
 Keep style and structure consistent across outputs.
Keep style and structure consistent across outputs.
3) Kling 3.0 vs Kling 2.6: The Side-by-Side Comparison
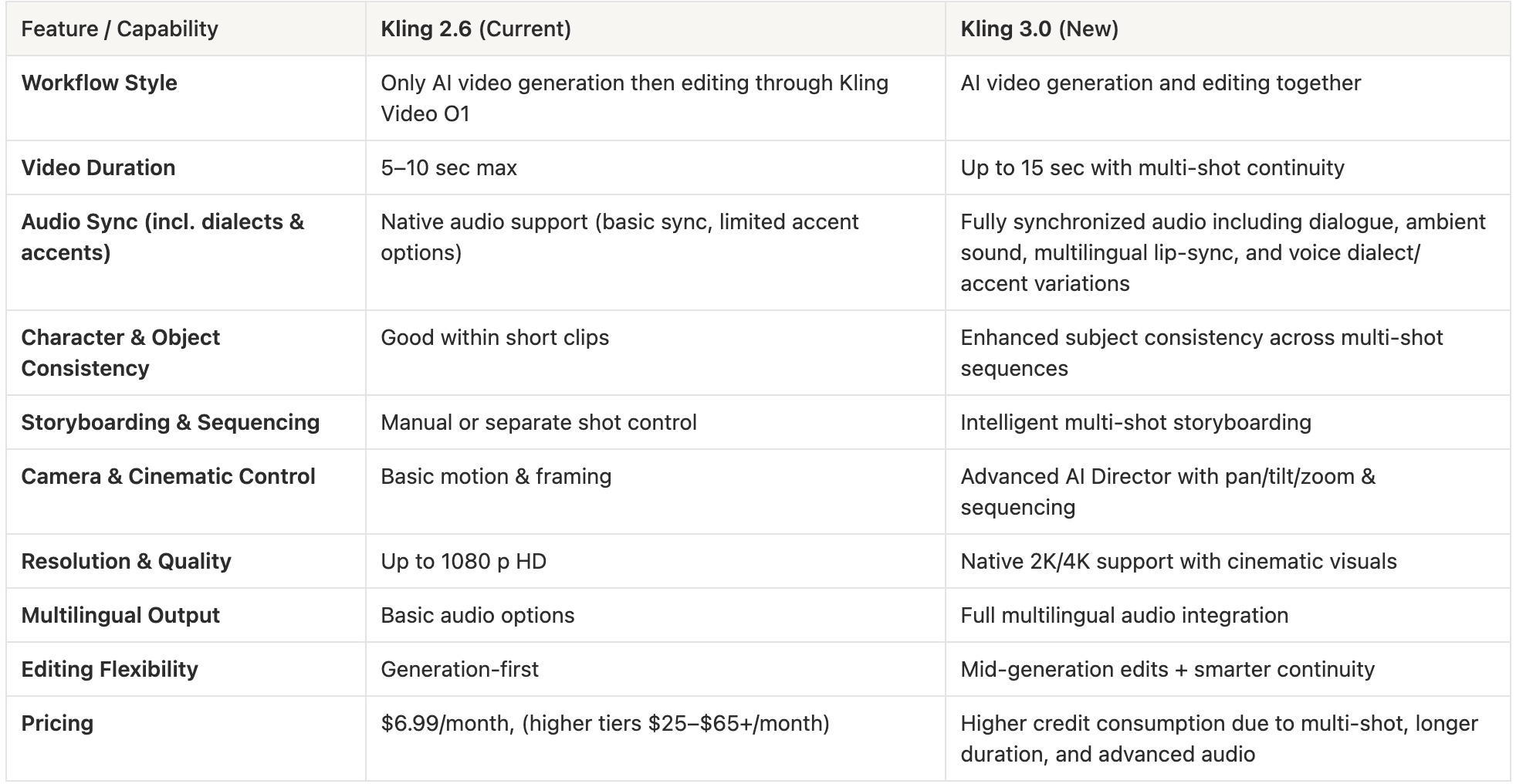 Kling 3.0 vs 2.6 Comparison: Which AI Video Model Wins
Kling 3.0 vs 2.6 Comparison: Which AI Video Model Wins
4) Stress-Test Prompts to Try on Kling 2.6 and Kling 3.0
 Prompt to try on Kling 3.0
Prompt to try on Kling 3.0
Use these prompts as controlled stress tests to see how each model behaves under pressure. They target identity, motion, lighting, and scene complexity — the exact areas where differences between Kling 2.6 and 3.0 become visible.
Character Consistency Under Emotional Change:
- Prompt: Tight cinematic portrait of a young performer reacting to good news. The character moves from a calm expression to a wide smile and a brief laugh while the camera slowly moves closer. Maintain identical facial structure, hairstyle, and skin detail throughout. Soft natural lighting, shallow depth of field.
Wardrobe Morphing During Motion:
- Prompt: Medium shot of a dancer turning in a flowing emerald coat inside a minimal studio. The fabric moves dynamically as the subject spins. Keep the coat’s color, texture, and design unchanged through the movement. Clean studio lighting, smooth tracking shot.
Precision Camera Direction Test:
- Prompt: Cinematic hallway scene of a person walking forward while the camera performs a slow arc from right to left, ending in a gentle zoom toward the subject. Maintain continuous, smooth camera motion with no sudden shifts. Realistic indoor lighting.
Chaos Resistance in Busy Scenes:
- Prompt: A traveler stands still in the foreground of a busy train station while crowds move rapidly behind. Keep the main subject sharp and visually consistent as background activity remains energetic. Ambient daylight with natural shadows.
Dynamic Lighting Transition Test:
Prompt: Close-up shot of a person walking from a dim interior into bright outdoor sunlight. Lighting shifts gradually across the face while identity and texture remain stable. Cinematic realism, soft lens response.
 Keep style and structure consistent across outputs.
Keep style and structure consistent across outputs.
5) Who Should Choose Kling 3.0 vs Kling 2.6?
If you’re deciding which model fits your workflow, use this framework:
Choose Kling 3.0 if you need:
- Recurring characters or AI influencers
- Cinematic storytelling continuity
- Production-ready polish
Choose Kling 2.6 if you prioritize:
- Rapid prototyping
- High-volume short clips
- Fast experimentation
Use both if you want optimization:
Testing both inside ImagineArt lets you balance speed and polish without locking into one pipeline.
6) Where Kling 3.0 Hits Hard: Real Creator Use Cases That Actually Matter!
This is where Kling 3.0 vs 2.6 stops being technical and starts mapping directly to creator work. These are the workflows where the upgrade either saves you time or upgrades your output in ways audiences notice.
AI influencers and recurring social personas
Consistent characters turn one-off clips into scalable identities.
- Kling 3.0 stabilizes faces and wardrobe across episodes
- Recurring personas become believable and monetizable
- Social series can run without visible identity drift
This is the foundation for character-driven channels. Once your AI persona is stable, you can scale distribution and campaigns using ImagineArt AI Marketing Tools to turn recurring characters into monetizable channels.
Cinematic storytelling and short-form films
Narrative work collapses if continuity breaks.
- Kling 3.0 maintains character persistence across scenes
- Multi-shot flow supports structured storytelling
- Camera control enables deliberate pacing
Short films and episodic sequences become more viable.
Branded content and UGC-style advertising
Commercial work needs repeatable visuals.
- Wardrobe and prop stability protect brand assets
- Cleaner audio sync improves demo realism
- Reduced regeneration saves production time
This fits ad campaigns and sponsored content pipelines.
Interactive media and game-style character content
Kling 3.0 enables creators to build consistent characters for interactive or game-adjacent media.
- Characters can appear across trailers, cutscenes, and promos
- Identity stability supports serialized world-building
- Visual continuity helps expand fictional universes
This connects AI video with gaming, virtual worlds, and character franchises.
5) Educational and explainer media
Instructional content depends on visual trust.
- Stable on-screen presenters improve credibility
- Smooth motion supports guided focus
- Consistent visuals reduce distraction
This supports tutorials, training, and learning media.
7) Early Access and Where You Can Test Kling 3.0 Right Now
After controlled testing, the gap between Kling 3.0 and 2.6 shows up in production-critical areas. Kling 3.0 doesn’t replace 2.6 in every scenario, but it clearly leads where polish and repeatability matter.
Kling 3.0 wins in:
- Character consistency across motion and multi-shot scenes
- Continuity without the reset feeling seen in 2.6
- Audio sync that lands closer to production quality
- Camera precision that follows prompts more faithfully
- Rendering stability at higher resolutions
Kling 2.6 still holds value for rapid experimentation and high-volume short clips. But when clips must survive close inspection, Kling 3.0 becomes the stronger default.
8) Performance Verdict: Where Kling 3.0 Actually Beats Kling 2.6
Kling 2.6 is not obsolete. It’s still one of the strongest AI video models for camera control, clean motion, and fast short-form production. Many creators can keep using it without friction. The difference is that in specific pressure scenarios — the ones that expose continuity and polish — Kling 3.0 pulls ahead by noticeable margins.
 Make interactive or game-adjacent media from Kling 3.0
Make interactive or game-adjacent media from Kling 3.0
Those margins show up here:
- Character consistency across motion and multi-shot scenes
Kling 3.0 locks identity more tightly when faces turn, expressions change, or scenes connect. In 2.6, a small drift can appear during transitions. In 3.0, the character holds together longer, which matters for recurring personas and narrative clips.
- Continuity without the reset effect
Multi-shot flow in 3.0 feels connected instead of stitched. Kling 2.6 still generates strong individual shots, but 3.0 maintains visual memory between them, which improves storytelling sequences.
- Audio sync is closer to production quality
Dialogue alignment in 3.0 sits tighter against motion. Kling 2.6 already handles audio well, but 3.0 reduces the cleanup you’d normally expect in edit.
- Camera precision and prompt adherence
Both versions offer solid motion control, but 3.0 follows complex camera instructions more faithfully. Directional prompts land closer to intent, especially in tracking shots.
- Rendering stability at higher resolutions
Under dense motion and lighting shifts, 3.0 preserves texture and detail more consistently. Kling 2.6 remains strong for standard clips, but 3.0 holds up better when visual polish is critical.
Kling 2.6 still makes sense for rapid experimentation and high-volume output. Kling 3.0 becomes the better choice when continuity, identity lock, and production finish matter. The upgrade isn’t about replacing 2.6 everywhere. It’s about tightening the exact areas where creators used to compensate in post.
9) What Comes After Kling 3.0: The Direction of AI Video
 Kling 3.0 vs Kling 2.6
Kling 3.0 vs Kling 2.6
Kling 3.0 doesn’t feel like an endpoint. It looks like a marker for where AI video generation is heading next. The trajectory is clear: longer scenes, tighter identity persistence, and deeper integration between generation and editing. Models are moving from clip factories toward systems that support structured storytelling and repeatable characters.
The next wave of AI video trends in 2026 will likely push:
- Longer continuous sequences with stable narrative memory
- Stronger character persistence across episodes
- More granular editing controls inside generation workflows
- Higher native fidelity without external post-processing
For creators, this means workflows will shift from isolated clip production to reusable character pipelines. Preparing now means building prompt libraries, testing identity templates, and structuring projects around repeatability. The next generation video AI won’t reward one-off experiments as much as it rewards scalable systems.
Get the Best of Both with ImagineArt
Kling 3.0 reads as a forward step, but it doesn’t erase Kling 2.6. The practical strategy is balance. Kling 3.0 works as an experimental upgrade layer. Kling 2.6 remains a stable production base.
Testing both inside ImagineArt gives creators a controlled path forward:
- Early exposure to Kling 3.0 capabilities
- A stable fallback in Kling 2.6
- Evidence-driven adoption instead of blind switching
That approach aligns with how serious creators evaluate AI video tools in 2026. You don’t commit based on hype. You test, compare, and integrate what proves reliable.

Umaima Shah
Umaima Shah is a creative content strategist specializing in AI tools, image generation, and emerging technologies. She focuses on translating complex platforms into clear, practical insights for creators, designers, and product teams